


Risk management encompasses the identification, analysis, and response to risk factors that form part of the life of a business, and it is usually done with its best interest in mind. Effective risk management means total control of future outcomes proactively rather than reactively. Therefore, effective risk management offers the potential to reduce both the possibility of a risk occurring and its impact.
Enterprise risk management (ERM) in business includes the methods and processes used by organizations to manage risks and seize opportunities related to the achievement of their objectives. ERM provides a framework for risk management, which typically involves identifying particular events or circumstances relevant to the organization's objectives (risks and opportunities), assessing them in terms of likelihood and magnitude of impact, determining a response strategy, and monitoring process. By identifying and proactively addressing risks and opportunities, business enterprises protect and create value for their stakeholders, including owners, employees, customers, regulators, and society overall.
ERM can also be described as a risk-based approach to managing an enterprise, integrating concepts of internal control, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, data protection and strategic planning. ERM is evolving to address the needs of various stakeholders, who want to understand the broad spectrum of risks facing complex organizations to ensure they are appropriately managed. Regulators and debt rating agencies have increased their scrutiny on the risk management processes of companies.
ERM Frameworks:
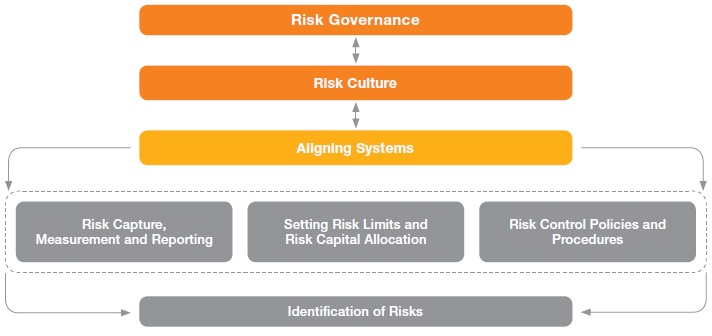
There are various important ERM frameworks, each of which describes an approach for identifying, analyzing, responding to, and
monitoring risks and opportunities, within the internal and external environment facing the enterprise.
Risk Responses:
Management selects a risk response strategy for specific risks identified and analyzed, which may include:
Risk Functions:
The primary risk functions in large corporations that may participate in an ERM program typically include:
Current issues in ERM
The risk management processes of corporations worldwide are under increasing regulatory and private scrutiny. Risk is an essential part of any
business. Properly managed, it drives growth and opportunity. Executives struggle with business pressures that may be partly or completely beyond
their immediate control, such as distressed financial markets; mergers, acquisitions and restructurings; disruptive technology change; geopolitical
instabilities; and the rising price of energy.
Common challenges include:
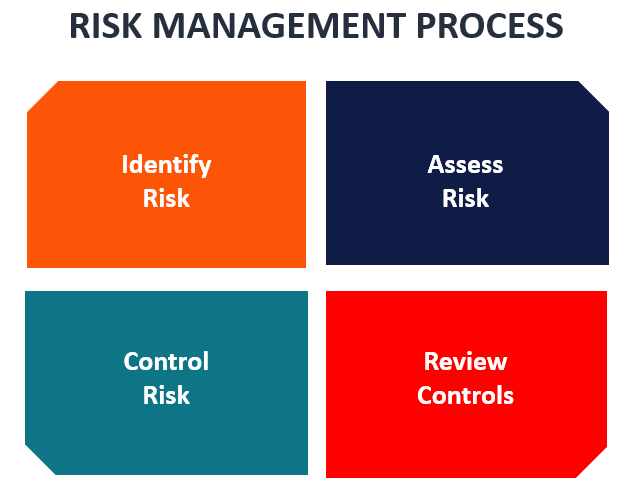
A risk management strategy provides a structured and coherent approach to identifying, assessing and managing risk or uncertainties followed up by minimizing, monitoring and controlling the impact of risk realities or enhancing the opportunity potential by applying coordinated and economical resources.
Our experts partner with clients on risk management, providing perspective not only on immediate value and impact, but on long-term implications. We work closely with management and other advisers to leverage and complement their knowledge and ensure maximum impact, and actively support implementation and skill building.
